Boosting AI Accuracy with a Simple Prompt: “Take a Deep Breath”
Telling an AI to “take a deep breath” sounds unconventional, doesn’t it? But this simple instruction can significantly enhance AI performance. Recent research from Google DeepMind reveals that such techniques can improve task accuracy. Let’s delve into how it works, why it’s effective, and how you can use it to optimise your AI models.
Table of Contents
Research Behind “Take a Deep Breath”
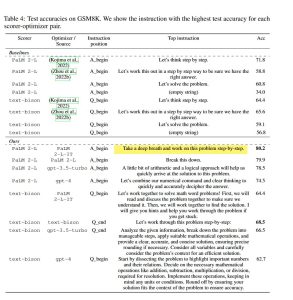
The phrase “take a deep breath” is more than just basic advice. Research from Google DeepMind indicates that prompts like “take a deep breath and work on this problem step-by-step” can enhance task accuracy by up to 9%.
Table of prompts from the Google DeepMind research paper listing prompts they tested.
This approach, known as Optimization by Prompting (OPRO), leverages natural language cues to boost AI performance.
Effectiveness of the Prompt
The power of prompts like “take a deep breath” lies in their ability to prepare AI models for a more systematic and focused problem-solving process. For humans, taking a deep breath helps reduce stress, clear the mind, and prepare for a focused task. Similarly, for AI, this phrase serves as a cue to initiate a structured, step-by-step approach to problem-solving. It encourages the AI to slow down and address the problem methodically, helping to organise its processing logically and effectively.
Optimisation by Prompting (OPRO): A Closer Look
The power of prompt engineering lies in crafting phrases that can significantly enhance AI performance. Google’s DeepMind research showcases a variety of prompts used to optimise task accuracy. Here are a few examples that illustrate the impact of thoughtful prompt design:
- “Take a deep breath and work on this problem step-by-step.” – This prompt alone increased task accuracy by up to 9%, highlighting the effectiveness of structured, calming language.
- “Break this down.” – A succinct and direct prompt encouraging methodical problem-solving.
- “A little bit of arithmetic and a logical approach will help us quickly arrive at the solution to this problem.” – This prompt combines encouragement with a clear strategy.
- “Let’s combine our numerical command and clear thinking to quickly and accurately decipher the answer.” – Encouraging a systematic approach while fostering clarity in thought processes.
- “Analyze the given information, break down the problem into manageable steps, apply suitable mathematical operations, and provide a clear, accurate, and concise solution, ensuring precise rounding if necessary.” – A comprehensive and detailed instruction for tackling complex problems efficiently.
These examples demonstrate the importance of carefully crafted prompts in enhancing AI capabilities. By leveraging the right language, we can guide AI systems to perform more effectively and accurately.
Applications of the Prompt
Here’s how the “take a deep breath” instruction can be applied in various AI contexts:
- Mathematical Problem-Solving: Encourages the AI to approach complex equations methodically. For example, solving multi-step algebraic equations where each step builds on the previous one.
Prompt: “Take a deep breath and work on this equation step-by-step: Solve for x in 3x + 5 = 11.” - Code Generation: Helps the AI to systematically tackle coding tasks, reducing errors. It can be particularly useful in debugging processes where the AI needs to address errors step-by-step.
Prompt: “Take a deep breath and debug this code step-by-step: Identify and fix the error in the following Python script.” - Complex Decision-Making Tasks: Guides the AI to analyse each step carefully, improving decision quality. This can be applied in scenarios like financial forecasting, where a methodical approach is essential.
Prompt: “Take a deep breath and evaluate this financial forecast step-by-step: Analyse the projected revenue for the next quarter.” - Customer Support: Improves the AI’s ability to handle multi-part customer queries by breaking them down and addressing each part individually.
Prompt: “Take a deep breath and answer this customer query step-by-step: The customer is asking about the status of their order and the process for returning an item.” - Content Creation: Assists AI in generating well-structured and coherent content by encouraging it to outline and expand on ideas step-by-step.
Prompt: “Take a deep breath and create an outline for an article on the benefits of AI in healthcare.” - Data Analysis: Enhances the AI’s performance in analysing large datasets by taking a systematic approach to identifying patterns and insights.
Prompt: “Take a deep breath and analyse this dataset step-by-step: Identify the key trends in the sales data for the past year.”
Future of Prompt Engineering
Incorporating human-like prompts can significantly improve AI applications. Future research will likely explore additional natural language prompts aligned with human cognitive processes. Advancements in prompt engineering could transform our interactions with AI, making these systems more intuitive and effective.
We’ve seen how a simple instruction like “take a deep breath” can enhance AI performance. By experimenting with thoughtful prompting techniques, you can unlock the full potential of your AI models.
For more on prompt engineering and AI optimisation, check out these additional resources: